Various Types of Pavement Marking on Road for Safety
A pavement marking is a marking that provides pedestrians and drivers with information and guidance on paved roads. They can be used in parking lots and other areas nominated for other purposes, such as designated parking areas. Additionally, they are used to show there are no parking pavement markings on the road.
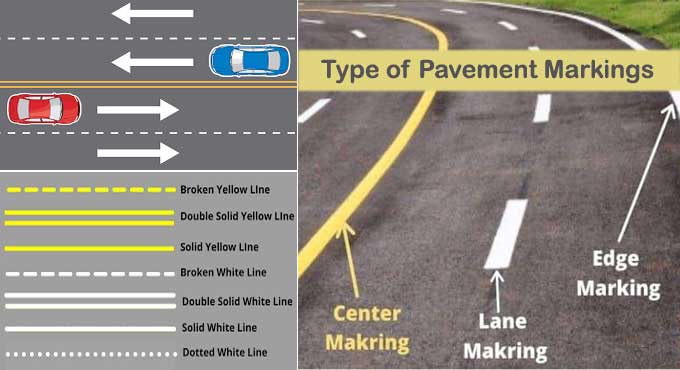
You can determine if the traffic is moving in one or two directions by seeing white or yellow lines dividing the lanes or marking the center of the road. White lines separate traffic lanes moving in the same direction from yellow lines.
Roadway striping does not apply to pavement markings. That is a factor in a guidance system for delivering regulatory and vehicle-path information beyond the requirement that users change their attention from the road.
Roadway markings are generally used to improve safety and increase efficiency. A pavement marking can only be effective if it can be perceived and understood easily. Every time a pavement marking is encountered, it is characterized by the same color, shape, and style.
Types of Pavement Markings
1. Longitudinal
Lines, edges, channelizing lines, and centerlines are common longitudinal markings adjacent to traffic flow. In addition to guiding traffic on a roadway, these markings also serve as a visual marker for travel lanes. Pavement markings such as this are among the best.
2. Yellow
Centerline yellow pavement markings for routes separated traffic lanes opposite to each other. It is possible to place these yellow pavement markings at locations that are not in the perfect center of the road. There may be times when it is necessary to paint centerline pavement road markings on certain sections of road to control traffic, such as where there are curves, hills, grade crossings, or bridges.
3. White lane Line
The same-directional traffic lanes are marked with white pavement markings. It recommends placing these markings adjacent to two or more traffic lanes in the same direction unless they are part of a reversible lane. The use of lane alignment markings recommends overcrowded areas which have more marked lanes than those with no markings.
Solid White Line
Its purpose is to instruct drivers to settle into a lane and to mark the shoulder of the roadway.
Broken White line
These broken white lines will include a lane marking excluding regions where crossing is permitted. Changing lanes is permitted on a broken white line as long as it is safe.
4. Edge line
An edge line pavement marking defines the edges of the roadway. When weather conditions are bad and visibility is low, these are useful visual guides. Intersections and major driveways should not have edge lines. If any of these things are true, then a solid yellow line can denote the left side of a divided highway, one-way street, or ramp. Roadside right-hand edges are usually defined by solid white lines. You may use wide solid edge line-markings at locations with an essential for greater visibility.
5. No-Passing Zones
Engineering studies indicating inadequate sight distance or other such reasons would call for no-passing zones on two-lane and three-lane roadways with centerlines.
6. Stop & Yield Lines
When approaching an intersection or mid-block crosswalk, stop and yield lines provide drivers with specific instructions on when to stop or yield. The yield line is known as the give way line and indicates where drivers expect to yield at an intersection or roundabout.
7. Roundabout
Circular intersections are defined as roundabouts. They design to maintain a controlled speed and offer specific traffic controls. A roundabout's pavement markings and signs must take into consideration the lane usage and geometric design.
8. Crosswalks
Pedestrians need crossing pavement markings to get to locations where traffic control is convenient, including traffic signals or school crossing guards. However, marked pedestrian crosswalks don't reduce pedestrian accidents or moderate traffic by themselves.
Pros of Pavement Marking
- No special equipment is required to install the pavement markings.
- The durability of markings depends on the quality of traffic and the length of its service life.
- There is the potential for high retro reflectivity.
- The environment is protected and there is little risk of worker and environmental injury from marking.
Cons of Pavement Marking
- Initial costs are higher for markings on pavements.
- A road in poor condition can be incompatible with this type of asphalt.
Conclusion
Good visibility should be provided by all pavement markings at all times. Municipalities are ultimately responsible for maintaining markings once they have installed them.
The documentation of the selection process must maintain if the municipality has decided to discontinue markings. It is important to remove road markings that are not applicable or complex as soon as possible.
In addition to signposts and signals, pavement markings are part of the intelligence system that helps drivers locate where to park, alert them to impending road conditions, and identify areas where vehicles are permitted to convey. You will benefit most from the white and yellow DMV tests and practice permits.
Download : Pavement Marking ? Types & How they Supplement Road Safety